
On the 45th anniversary of the Apollo 11 landing, Phil Plait wonders what the hell happened to the Dream of Space in America. “Venturing into space is not just something we can do. It’s something we must do.”
Haunting the Web Since 1999

On the 45th anniversary of the Apollo 11 landing, Phil Plait wonders what the hell happened to the Dream of Space in America. “Venturing into space is not just something we can do. It’s something we must do.”
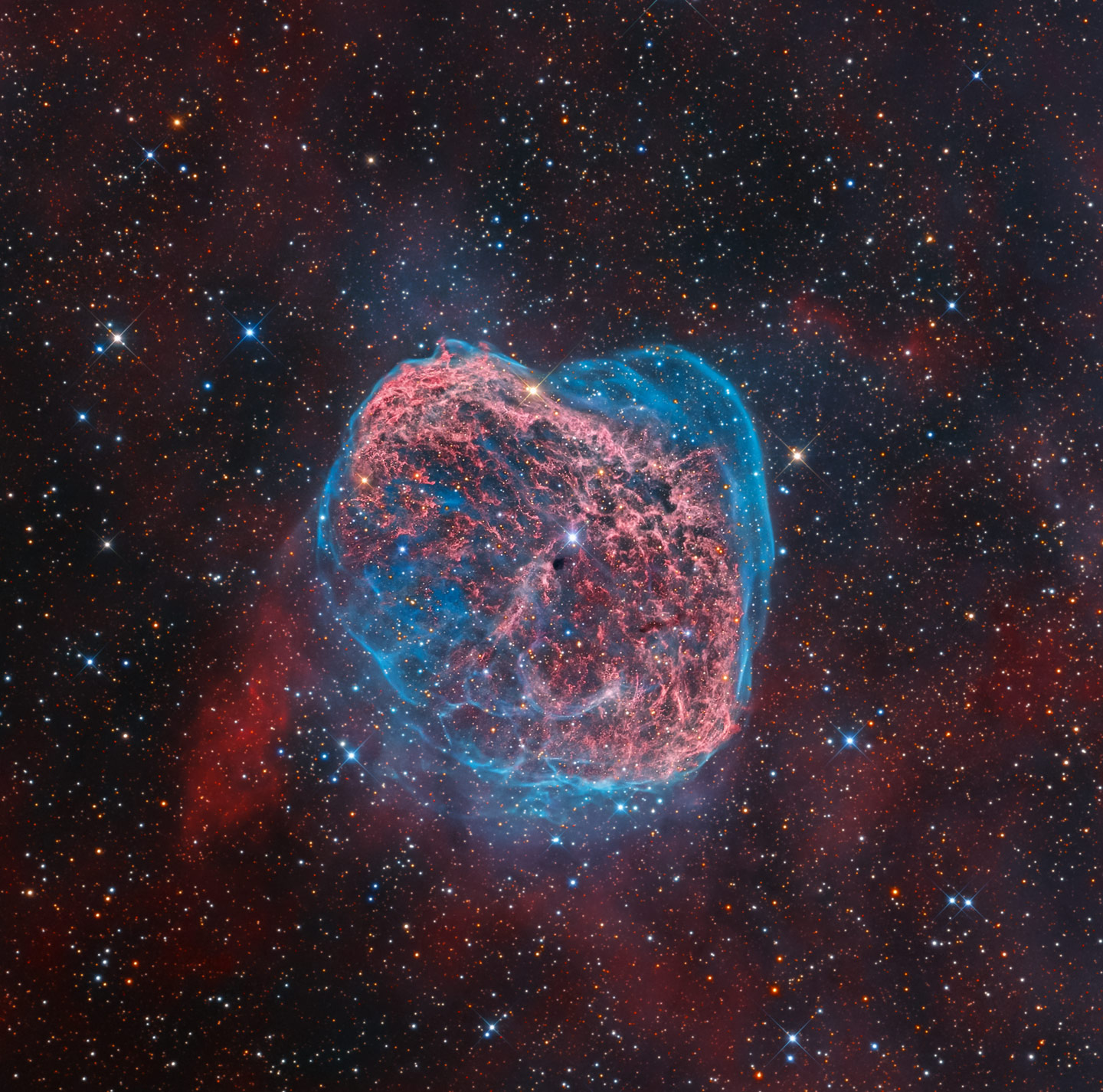

From attack ships on fire off the shoulder of Orion to c-beams glittering in the dark near the Tannhauser Gate, Slate’s Phil Plait shows off the winners of this year’s Astronomy Photographs of the Year. All 2500 submissions can be viewed here.

By way of Dangerous Meta, did Dark Matter kill the dinosaurs? Extremely speculative here, but food for thought. “The European Space Agency’s Gaia mission, which launched last year, will map the gravitational field of the Galaxy and could rule out or confirm the presence of this darker disk.”

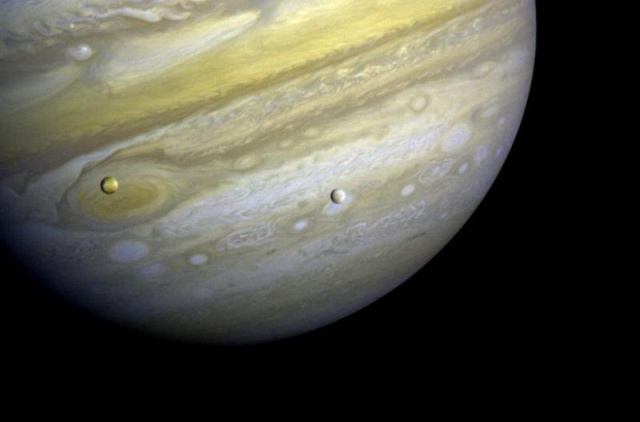
NASA sets aside some money for a robotic mission to Europa. “No details have been decided yet, but NASA chief financial officer Elizabeth Robinson said Tuesday that it would be launched in the mid-2020s.”
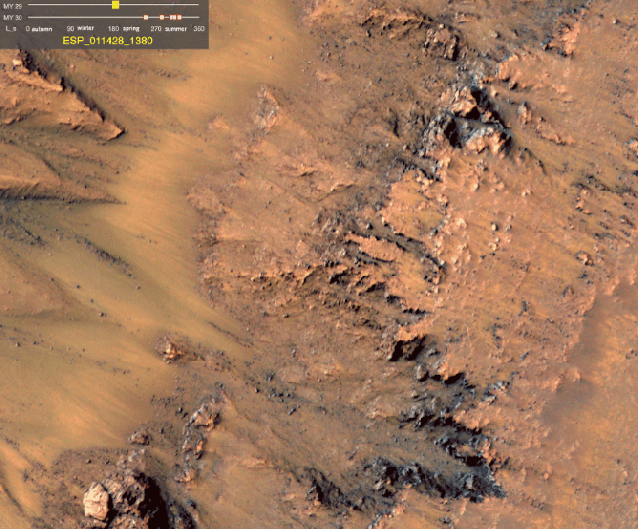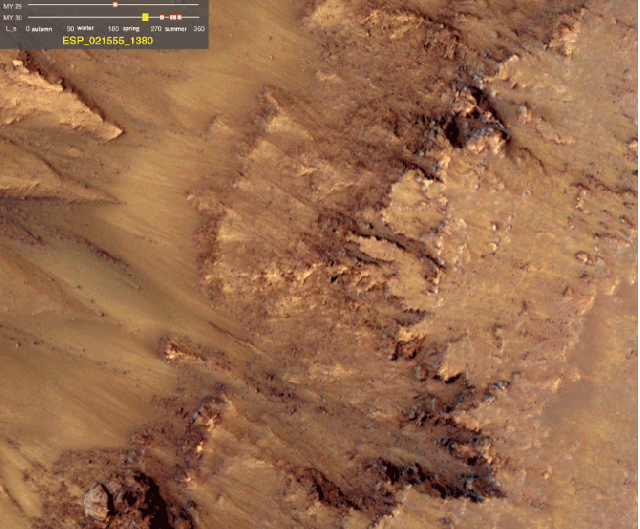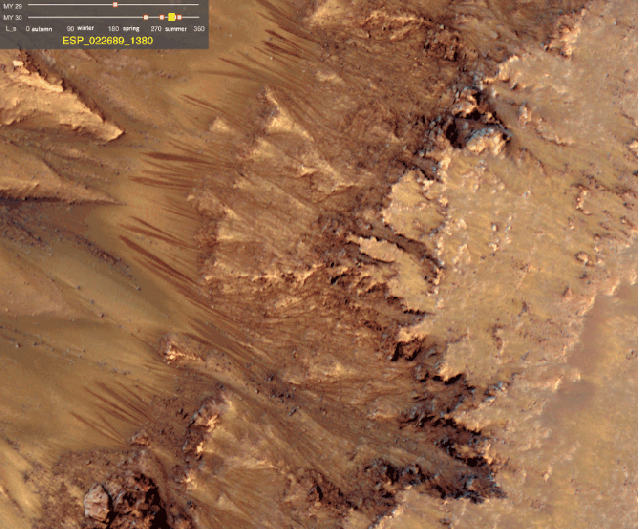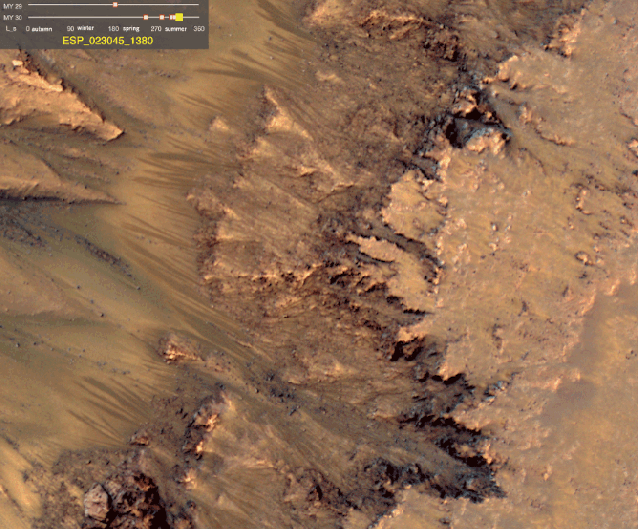
Via io9, Scientists at NASA’s JPL find the strongest evidence of currently extant water on Mars yet. “We still don’t have a smoking gun for existence of water…Although we’re not sure how this process would take place without water.”



Because of sequestration and other budget cuts, NASA is forced to cancel its advanced spacecraft power program, threatening future missions past the asteroid belt. “ASRGs had been under development by NASA for over a decade, and had been planned for use by 2016 in the next low-cost planetary exploration missions…Because of the limited cost cap imposed on these missions, they’re now essentially limited to the inner solar system. Missions with bigger budgets that could afford regular RTGs will be bottlenecked by the production rate of Plutonium to maybe once or twice per decade. Goodbye, outer planets.”
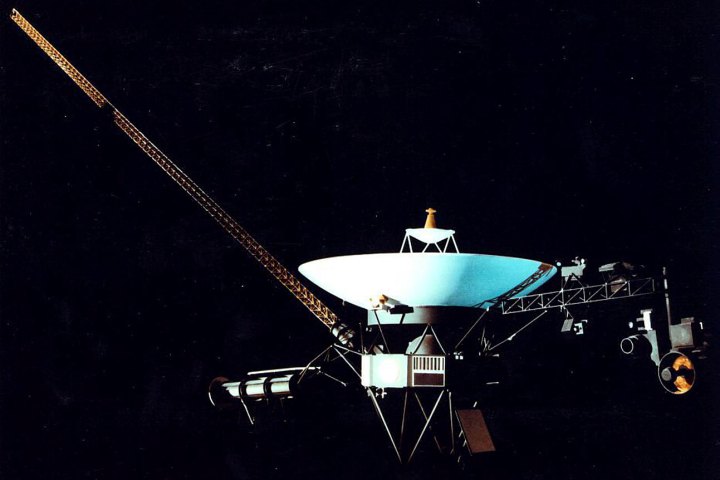

It’s been out in the fringe territories for a few years, but apparently now it’s official: Voyager I has left the Solar System. “We’re in a new region. And everything we’re measuring is different and exciting.”
Update: Belay that- NASA’s Voyager team says hold the champagne: “In December 2012, the Voyager science team reported that Voyager 1 is within a new region called ‘the magnetic highway’ where energetic particles changed dramatically. A change in the direction of the magnetic field is the last critical indicator of reaching interstellar space and that change of direction has not yet been observed.”

An auspicious site for New Rome: Seven hills on Mars are named after the fallen astronauts of Columbia. “Spirit would go on to spend several years exploring the Columbia Hills until, struggling in the Martian soil, it would finally cease to function in 2010. Which — striving and striving, until you can strive no more — seems an appropriate tribute to seven people who gave their lives so that the rest of us might forge ahead.”