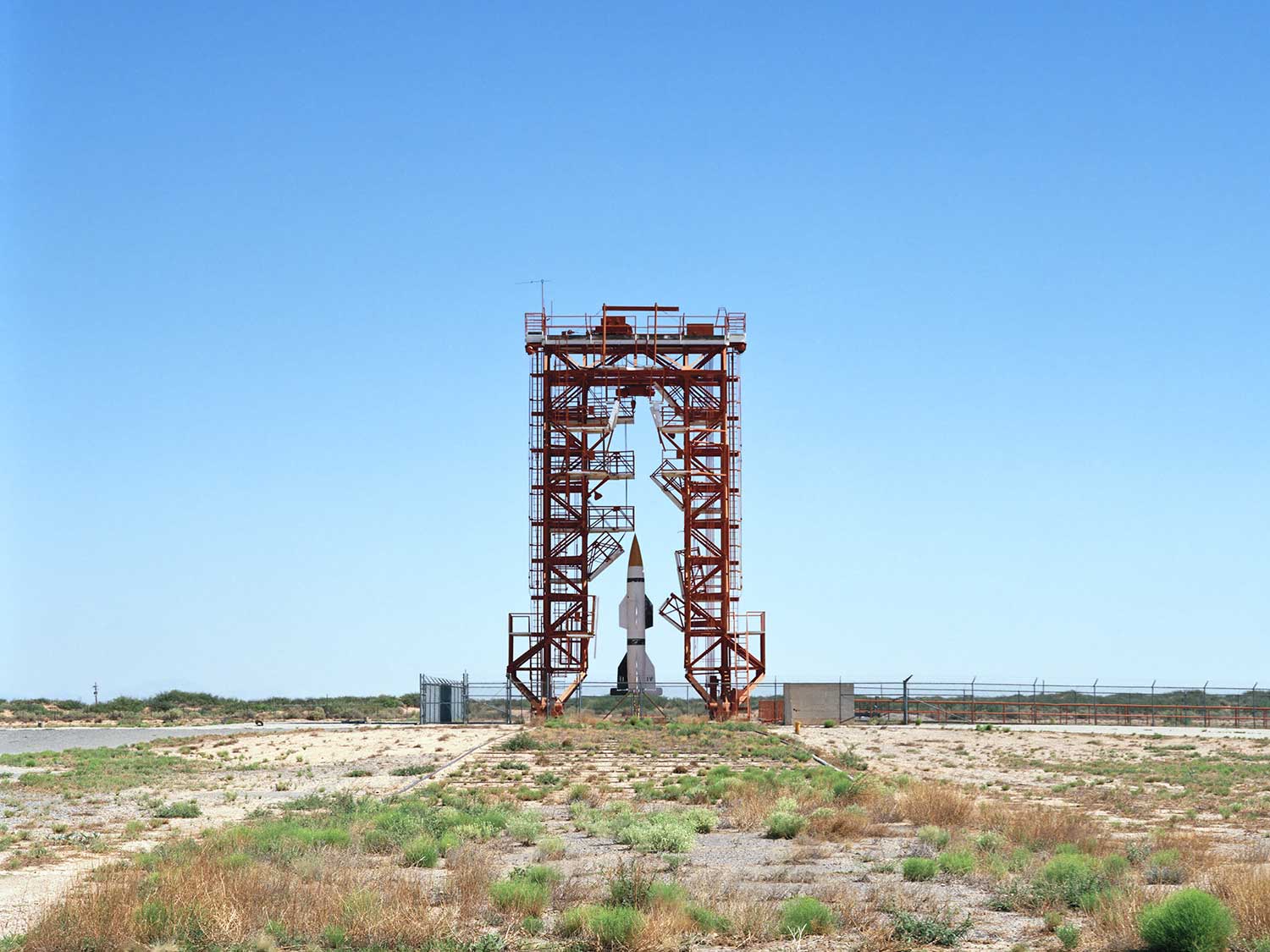
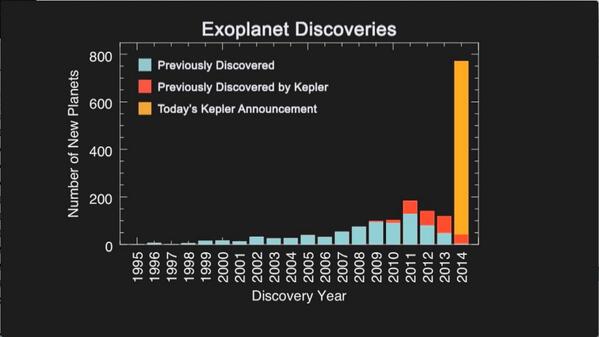
In Wired, photographer Roland Miller captures the decaying infrastructure of the early space race. “As launch pads were replaced, retrofitted or decommissioned, Miller was invited inside. By his estimate, 50 percent of the things he’s photographed no longer exist. ‘It’s not in NASA’s mission to conserve these sites,’ he says. ‘With shrinking budgets it’s an impossible thing to do.'”
“There’s not only last week’s deadly crash by Virgin Galactic, which hoped to launch widespread space tourism, or the unexpected explosion of a rocket headed toward the International Space Station. The United States also retired the space shuttle fleet in 2011. And…we now spend less on NASA — relative to the wealth of overall economy — than at any point in history.”
In very related news, and in the wake of Interstellar (which, on account of all the reasons I just mentioned, I haven’t seen yet), the Post‘s Zachary Goldfarb briefly surveys our current neglect of the space program. (Here’s what we’ve got planned at the moment.) “As recently as 2012, polling showed that more Americans than ever before thought that we were spending too little.”